OVUG section: Enterprise Voice
Today we are the lucky owners of a fully functional OCS environment connected to Interoute One Services.
For a while Interoute ![]() is one of our partners in iSIP services. A couple of month's ago e-office connected LCS to the iSIP cloud. The 16th of October interoute is fully supporting OCS2007RTM and ofcourse federation. Even interoute One is supporting OCS and MOC.
is one of our partners in iSIP services. A couple of month's ago e-office connected LCS to the iSIP cloud. The 16th of October interoute is fully supporting OCS2007RTM and ofcourse federation. Even interoute One is supporting OCS and MOC.
What is interoute One?
Interoute One is an advance VoIP solution, the core of which is the integration to Microsoft Office Communications Server. It acts as a secure communications clearing house, creating a global community of Microsoft Office Communicator (MOC) users. Alternative solutions include a stand alone soft phone and integration into existing IP or TDM PBX devices.
Traditional network:
cons:
- Complex
- Expensive
- Lack of expertise
pros:
- Simple Online Setup
- Zero cost
- Auto Configured
The main question is how can i configure OCS to connect to Interoute One.
Basically you need to do the following steps:
Step 1.
Login as new user of Interoute One. Make sure you have the DNS-name of your company present. Link Sing-Up for FREE!
Domain Name: This is the 'Sip domain' that your users are configured to use. If the user name is like user@company.com, the domain name is company.com. Most of the time this domain name is the same as the corporate SMTP domain space.
Step 2.
Interoute One will send you a loginname and password. Login at Interoute One Login Page:
Example is shown:
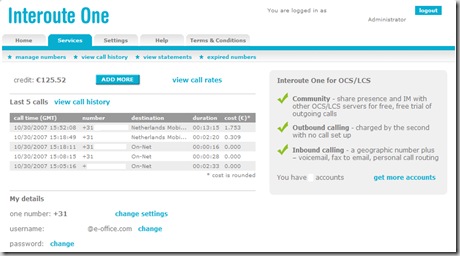
After fillin in the required information you will see the control panel every user have when using the Interoute One service.
Example is shown:
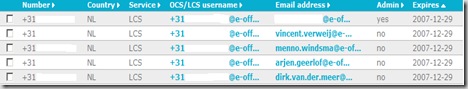
Be able to manage all your existing numbers:
Key features:
- one credit for all your available accounts. In our example: €125,52 euro.
- call hostory (duration, number called, call time)
- which services are enabled: Community,Outbound Calling and Inbound Calling.
- call rates and much more....
Step 3.
Make sure an OCS Mediation Server is installed and joined to the domain for example (contoso.local). A Mediation Server must be able to pass SIP requests and media between the Enterprise Voice infrastructure and a media gateway connected to the PSTN.
Assign this Mediation Server 2 separate NIC's with each a separate IP addresses. Configure one IP address to listening for Office Communication Server traffic. Configure the other NIC for listening for voice gateway traffic. There can only be one default gateway! Set it on your external edge of your Mediation Server.
Make sure your internal pool name is filled in (example: pool1.contoso.local) and make also sure that the PSTN next hop address is correct. In your case the PSTN next hop address is the public IP address of the Interoute One servers (89.*) this information fill be provided by Interoute in case you have any questions about that.
Step 4.
Make sure within the OCS Management Console that only users prepared as Enterprise Voice users are checked with the Enterprise Voice option and that the line URI is filled in. Example (+312......) You can configure Enterprise Voice on per user basis.
Step 5.
Make sure all users who are using Enterprise Voice have installed Microsoft Office Communicator 2007 (MOC2007).
Step 6.
Make sure numbers entered in MOC2007 can normalized to E.164. The format of the telephone number associated with the UC-enabled user is E.164 (example: +123456789). Therefore, if a user enters a number that is in different format (example: extension 1234) it has to be manipulated into the E.164 format.
OCS will take this number and search the corporate directory to find the user who has a matching number and then voice mail will be routed to the correct user. OCS uses normalization rules to translate these number formats and uses an internal translation service to perform canonicalization transformation. In our case we use only one normalization rule.
Step 7.
Check your Forest Level Voice Settings
To view global settings for Enterprise Voice:
- Open the Communications Server 2007 administrative snap-in.
- In the console pane, click the forest node.
- In the details pane, click the Voice tab.
- Expand one or more of the following to view the corresponding settings for Voice: Global Policy, Phone Usages, Normalization Rules, Location Profiles and Routes.
Step 8.
Check your pool level Voice Settings
To To view voice settings for a pool:
- Open the Communications Server 2007 administrative snap-in.
- In the console pane, click the pool whose settings you want to view.
- In the details pane, expand Voice Settings. Voice Settings displays pool-level settings for phone lock, location profile, and quality of service.
- Expand the settings you want to view.
Step 9.
Check your Route within OCS. When Communications Server determines that a dialed number needs to be routed to a PSTN gateway, the routing table is queried to determine the optimal gateway for the call. In our case the route is (.*) because we only have 1 normalization rule. So there is no need for logic routing.
Step 10.
Open ports on your FW (only outbound) only to the specific public IP addresses of Interoute (89.*) When configuring the Mediation Server, you are advised to accept the default media port gateway range of 60,000 to 64,000. The default range media port range enables the server to handle up to 1,000 simultaneous voice calls. We as e-office expanded this range.
11. Open ports on your FW (only inbound) only to your external edge of the Mediation Server. Ports (60,000-64,000).
12. There you go! Outbound calling will go through the services of Interoute One. Inbound calling will be forwarded to your OCS infrastructure. All: cheap, easy to use and just perfect! Sign it up for free and do not hesitate to contact me if you have any questions.