Question(s):
since some weeks I follow your blog about OCS on unified-communications.blogspot.com and I appreciate your work very much.
I am desperatly looking for information about how OCS clients communication flows over the network:
For example a OCS user on a OCS server in Europe makes an IM communication with another OCS user on a OCS server in the same organization in the USA.
- 1. I found that the SIP communication and the content oft he instant messages flows via the OCS servers and Video and Audio Streams flow directly from client computer to client computer?
- 2. But how are Video and Audio streams for Live Meetings flowing And how are the streams for voice calls flowing? And how are those streams flowing for remote, federated and internet (=public IM) users?
Anwsers:
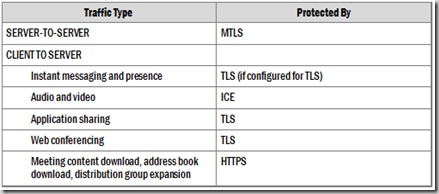
- 1. That’s true SIP Communications are routed between the OCS infrastructure you deployed. While using TLS and default MTLS the flow is as follows. TLS and MTLS protocols provide encrypted communications and endpoint authentication on the Internet. Office Communications Server uses these two protocols to create its network of trusted servers and to ensure that all communications over that network are encrypted. All SIP communications between servers occur over MTLS. SIP communications from client to server occur over TLS.TLS enables users, through their client software, to authenticate the Office Communications Server 2007 servers to which they connect. On a TLS connection, the client requests a valid certificate from the server. To be valid, the certificate must have been issued by a CA that is also trusted by the client and the DNS name of the server must match the DNS name on the certificate. If the certificate is valid, the client trusts the server and opens the connection. The resulting connection is trusted and from that point is not challenged by other trusted servers or clients. Default this is port 5061 TLS port or you can configure port 443. Server-to-server connections rely on MTLS (Mutual TLS) for mutual authentication. On an MTLS connection, the server originating a message and the server receiving it exchange certificates from a mutually trusted CA. The certificates prove the identity of each server to the other. In Office Communications Server 2007 deployments, certificates issued by the enterprise CA are automatically considered to be valid by all internal clients and servers. In federated scenarios, the issuing CA must be trusted by both federated partners. Each partner can use a different CA, if desired, so long as that CA is also trusted by the other partner.
- The following figure shows how Office Communications Server uses MTLS to create a network of trusted servers.
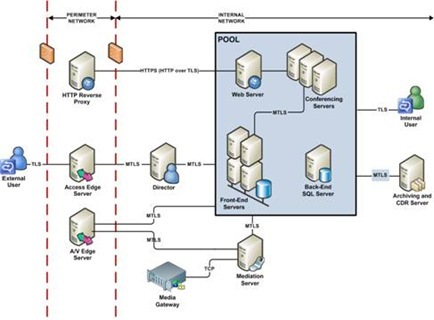
- Office Communications Server 2007 uses TLS and MTLS to encrypt instant messages. All server-to-server traffic requires MTLS, regardless of whether the traffic is confined to the internal network or crosses the internal network perimeter. Requirements for client-to-client traffic depend on whether that traffic crosses the internal corporate firewall. Strictly internal traffic can use either TLS, in which case the instant message is encrypted, or TCP, in which case it is not.
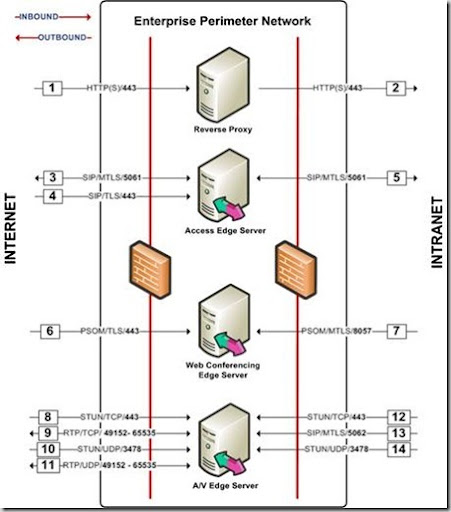
- But how are Video and Audio streams for Live Meetings flowing And how are the streams for voice calls flowing? The Video and Audio streams are redirected through your Edge infrastructure even to Federated partners. To get a good overview over which ports you need to open review. The first thing you need to do is consider which Edge infrastructure needs you have. When having that information review the OCS Edge Server deployment documentation.
- When looking at Enterprise Voice is an implementation of IP telephony that uses SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) for signaling and RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol) for voice. To get more controle over your Mediation Server and connections to a public PSTN cloud review my earlier post on how to configure the Mediation Server and Interoute see: post
- 2. But how are Video and Audio streams for Live Meetings flowing And how are the streams for voice calls flowing? And how are those streams flowing for remote, federated and internet (=public IM) users?
Important notice about connections to PIM:
If you enable public IM connectivity, be aware that while communications between Office Communications Server and the public IM server are encrypted, communications between the public IM server and the public IM client might not be encrypted, depending on whether encryption is provided by the public IM provider.


3 comments:
Good info, would be good to breakdown the 2nd question more for purely internal AV and Web conferences e.g. across a Global corp with 3 datacenters & where a conference had a spread of users whose home front end servers were in their local datacentre. Believe others would connect to the one conference host server of the meeting organizer
Hello all,
This is my very first topic here and was hopeing you can provide me with some assistance. I ran acorss your board as a resource for security information and hence was hopeing if you could please help by providing your input on office communication server technolgy risks. Have anyone worked on implementing OCS and is familiar with associated risks? Are there are any further known Federation risks in term of federating OCS with other companies for communication?
Please let me know if you have any resources that you would like to point for references. Thanks in advance.
Cheers,
Mondy
Post a Comment